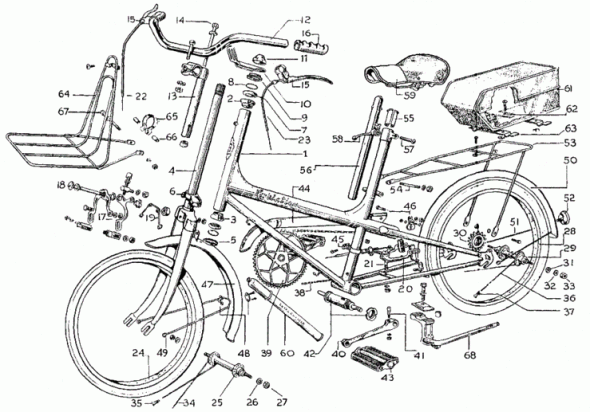
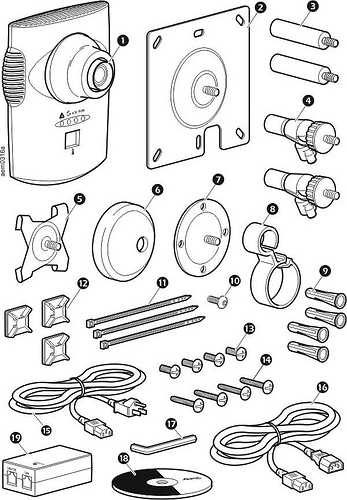
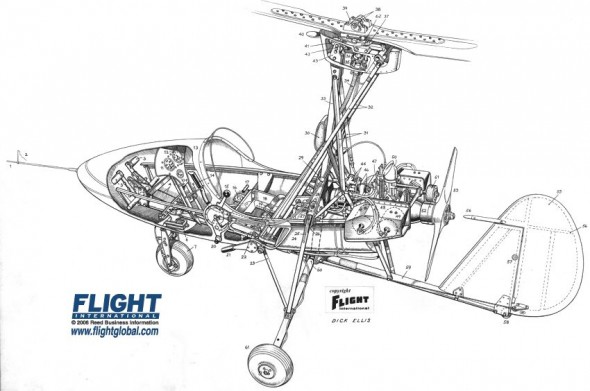
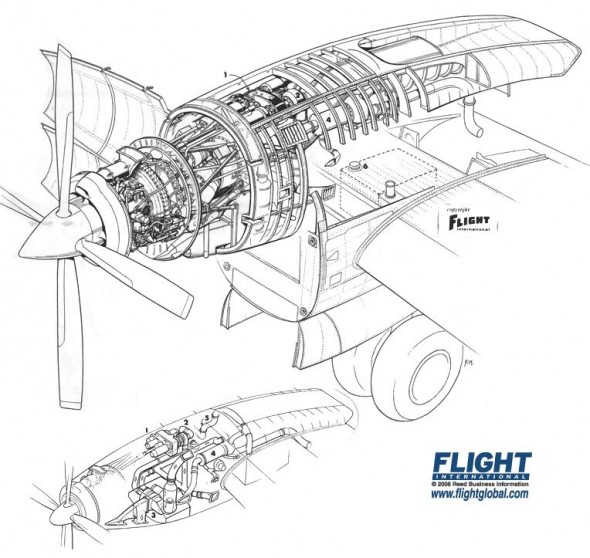
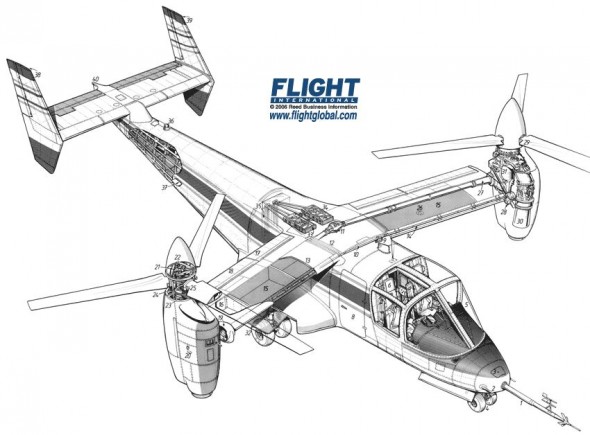
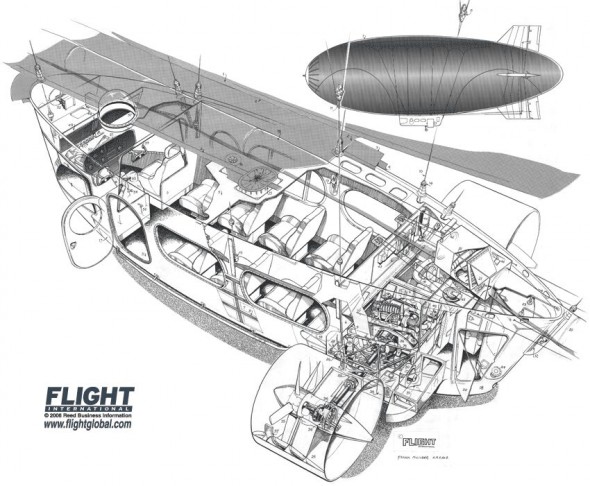
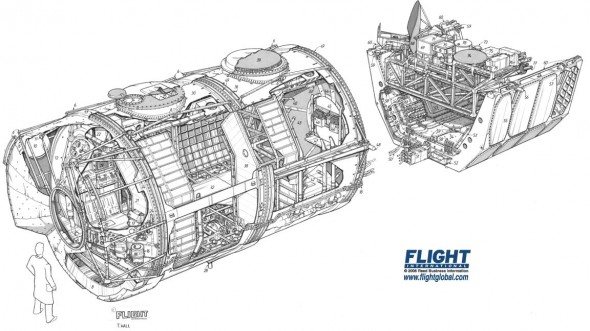
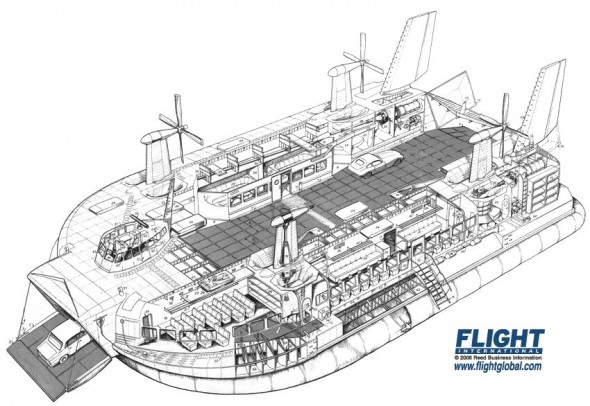
I’ve been meaning to write about style — the design and arrangement of visual elements that creates a tone or voice in an illustration, throughout a project, or across an illustrator’s entire body of work. More specifically, how style conflicts and complements with a technical illustrator’s role of visual communication.
This critique of dozens of newspapers’ adaptations of an Associated Press graphic serves as a great introduction to the topic. News graphics veteran Charles Apple dissects the minute decisions made by the various papers’ editors in the name of visual appeal, visual communication, story telling and branding.
Is technical illustration more about visual communication or style?
How do you compromise between the two?
[A Look at Tuesday’s Graphics-Heavy bin Laden Presentations]